How to Test Pool Water Chemistry
Proper pool water chemistry is essential for a clean, safe, inviting swimming environment. The most critical aspect of pool water maintenance is balancing the pH and chemical levels. Proper pH levels ensure that pool sanitizers, like chlorine, work efficiently and that the water is comfortable for swimmers. This guide will provide a detailed breakdown of maintaining the correct pH and chemical balance in your pool, covering essential elements like free chlorine, alkalinity, calcium hardness, and cyanuric acid (CYA).
Why Proper Pool Chemistry is Essential
Pool water chemistry plays a critical role in ensuring the cleanliness and safety of your pool. The correct pH and chemical balance protect swimmers from irritants like eye or skin discomfort and prevent damage to your pool equipment and surfaces. If your pool's pH or chemicals are out of balance, it can lead to various issues like:
- Corrosion of pool equipment and surfaces.
- Growth of algae and bacteria.
- Reduced effectiveness of sanitizers like chlorine.
- Cloudy water and unpleasant odors.
A well-maintained pool doesn't just look great—it's also safer and more enjoyable for swimmers. By understanding and maintaining the right balance, you will protect both your pool and your investment in the long run.

Understanding Pool Chemistry: Key Components
Before diving into the specifics of balancing pool water chemistry, it's essential to understand the key components that make up the ideal chemical balance in your pool:
pH Levels
The pH level measures the acidity or alkalinity of your pool water. Pool water that is too acidic (low pH) or alkaline (high pH) can cause problems. Ideally, your pool's pH should be between 7.2 and 7.6, considered the optimal range for pool water.
- Low pH (< 7.2): This can irritate the eyes and skin, damage pool equipment, and accelerate chlorine's effectiveness.
- High pH (> 7.6): Alkaline water can cause cloudy water and reduce the sanitizing power of chlorine, leading to algae growth.

Chlorine Levels
Chlorine is the most commonly used sanitizer for pools. It helps eliminate bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, keeping the water clean and safe. The ideal free chlorine level in pool water is between 1 and 3 ppm (parts per million). Keeping the chlorine levels balanced is essential for the pool's overall sanitation.
Total Alkalinity (TA)
Total alkalinity helps stabilize your pool's pH level. It acts as a buffer that keeps the pH from fluctuating too much. The ideal range for total alkalinity is between 80 and 120 ppm. If your alkalinity is too low, the pH will be unstable and difficult to control. Conversely, the pH may become too alkaline if it's too high, leading to cloudy water and scale buildup.
Calcium Hardness
Calcium hardness indicates the amount of calcium in the water and is crucial for avoiding scaling caused by high levels or corrosion due to low levels. Ideally, calcium hardness should stay between 200 and 400 ppm. Insufficient calcium hardness can damage pool surfaces and equipment, while excessive levels can lead to scaling on pool walls and equipment.
Cyanuric Acid (CYA)
Cyanuric acid, a pool stabilizer or conditioner, is used in outdoor pools to protect chlorine from the sun's ultraviolet rays. It acts as a sunscreen for chlorine, reducing its breakdown due to UV exposure. The ideal CYA level is between 30 and 50 ppm. Too much CYA can cause chlorine to become less effective, leading to poor sanitation, while too little can result in rapid chlorine degradation.
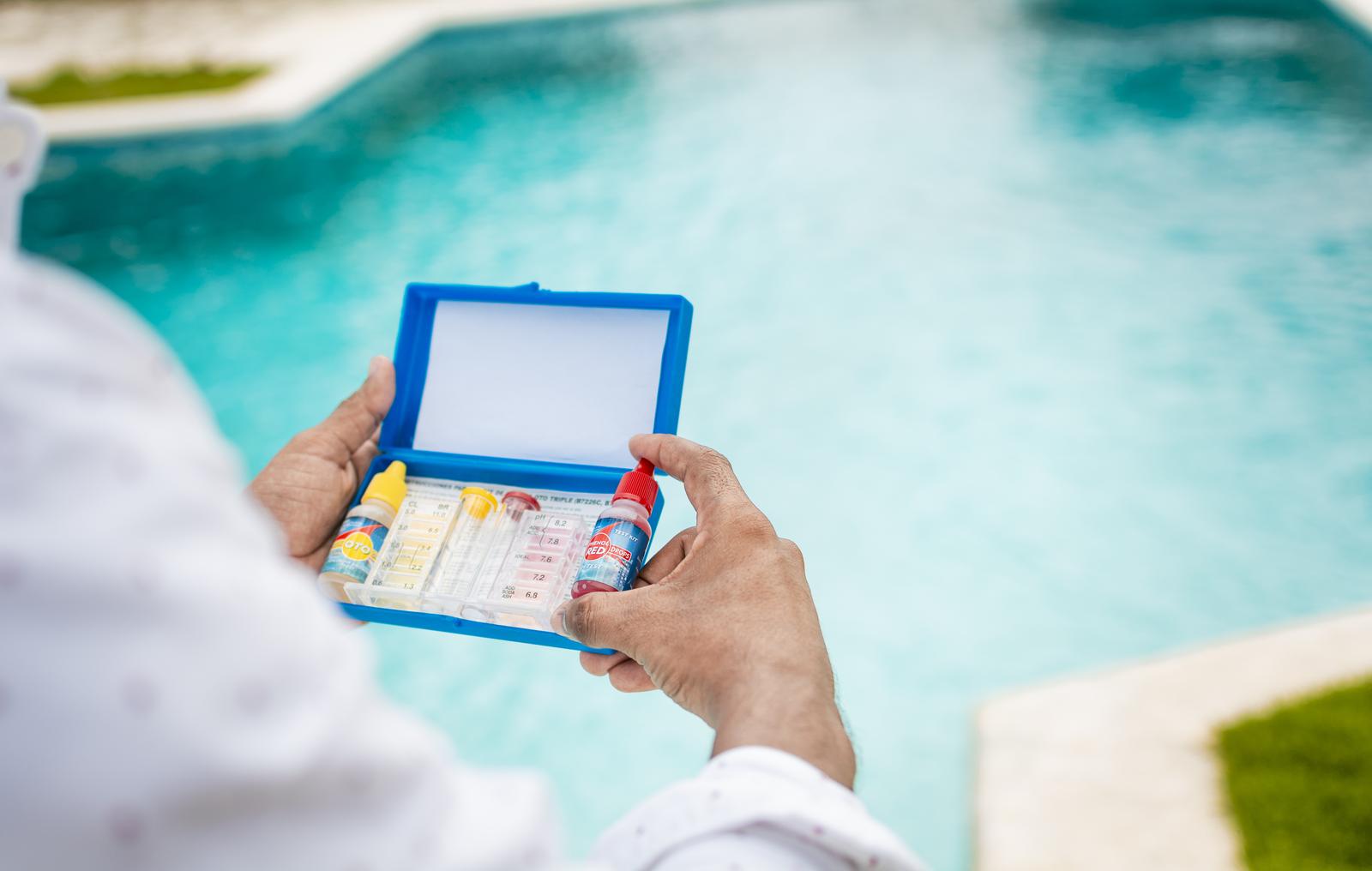
The Process of Testing Pool Water Chemistry
Testing your pool water is the first step in maintaining the proper pH and chemical balance. There are several methods for testing pool water, each with advantages and disadvantages.
Test Strips
Test strips are one of the easiest and quickest ways to measure pool water chemistry. To use a test strip, dip it into the water and wait for it to change color. The strip usually has a color chart that allows you to compare the results and determine the chemical levels. Test strips are convenient for routine testing but can be less precise than other methods.
Liquid Test Kits
Liquid test kits are more accurate and provide a detailed breakdown of pool chemical levels. They usually involve adding a reagent to a water sample and then observing the color change. This method is ideal for more comprehensive testing, allowing for a broader range of tests and precise measurements.
Digital Pool Testers
Digital pool testers are available for those who want a more advanced and precise method of testing. These testers use electrochemical sensors to provide an accurate reading of the pool's chemical levels. They are reliable but can be expensive.
Adjusting Chemical Imbalances in Your Pool
Once you have tested your pool water and identified imbalances, it's time to make the necessary adjustments.
Balancing pH
To raise the water's pH, you can add soda ash (also called sodium carbonate). Muriatic acid or dry acid is typically used to lower the pH. Always add the chemicals slowly and retest the water after 4-6 hours to see if further adjustments are needed.
Managing Chlorine Levels
If the pool's chlorine level is too low, add liquid chlorine, granular chlorine, or chlorine tablets. If it is too high, allow the pool to sit uncovered in the sun for a day or dilute the water by adding fresh water.
Adjusting Alkalinity
Baking soda can raise total alkalinity. To lower it, slowly add muriatic acid or dry acid, following the same method used to adjust pH.
Controlling Calcium Hardness
If the calcium hardness is too high, use a calcium hardness reducer to bring it down. If it's too low, add calcium chloride to increase the hardness.
Managing Cyanuric Acid (CYA)
To reduce high CYA levels, partially drain the pool and refill it with fresh water. If the levels are too low, cyanuric acid can be added directly to the pool.
Maintaining Pool Chemistry with Regular Testing
Consistency is key when it comes to pool maintenance. Testing your pool water chemistry at least once a week is essential to ensure that the pH and chemical levels stay within the ideal ranges. If your pool is heavily used, or if there have been significant changes in the weather (e.g., heavy rain or intense sun exposure), you may need to test the water more frequently.

Tips for Effective Pool Maintenance
To keep your pool chemistry in balance, consider these best practices:
- Keep a Regular Schedule: Establish a routine for testing and maintaining your pool water. Make it a habit to check pH and chlorine levels weekly.
- Use Quality Chemicals: Always use high-quality pool chemicals and ensure they are stored in a cool, dry place.
- Keep Your Pool Clean: Regularly clean your pool's filter, skimmer, and surface to prevent debris from affecting your water chemistry.
- Monitor Pool Usage: Increased usage or high temperatures can alter the chemical balance. Be proactive in testing when changes occur.
Common Pool Water Problems and Solutions
Cloudy Water
Cloudy water is often caused by imbalanced pH or high calcium hardness. The solution is to test the water and adjust the pH and calcium levels as needed. Regularly cleaning the pool filter also helps.
Algae Growth
Algae blooms thrive in poorly balanced pool water, particularly if chlorine levels are low. To prevent algae growth, shock the pool with a high dose of chlorine and clean the pool thoroughly.
Corrosion and Staining
Corrosion and staining are common when calcium hardness or pH levels are too low. Raising calcium hardness with calcium chloride and adjusting pH levels with muriatic acid will help prevent these issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How often should I test my pool water?
Testing your pool water at least once a week is recommended, especially during peak swimming seasons. You may need to test more frequently if your pool experiences high usage or extreme weather conditions.
What is the ideal pH for pool water?
The ideal pH range for pool water is between 7.2 and 7.6. This range ensures that chlorine works efficiently and the water is comfortable for swimming.
How can I raise the alkalinity of my pool water?
To raise alkalinity, add baking soda to the pool water. Follow the manufacturer's instructions and retest the water after a few hours.
What is cyanuric acid, and do I need it in my pool?
Cyanuric acid stabilizes chlorine in outdoor pools. It prevents sunlight from breaking down chlorine, ensuring that it lasts longer and maintains proper sanitization levels.
